When Did Ancient Egypt Start and End? Know the secrets

- Nov 24, 2024
- Ancient Egyptian Civilization
- 4,957
Ancient Egypt is, without a doubt, one of the largest ancient civilizations that has ever existed in the history of mankind. It is a civilization that thrived for about 3000 years along the great Nile and made a significant imprint in art, political structure, and religion. However, when did ancient Egypt start and end, and what caused its downfall?
In this article, you will learn how Ancient Egypt began, who its famous Pharaohs were, and what life was like for the average Egyptian. We will also explore this ancient society's beliefs, food, and geography.
Table of contents [Show]
- When Was Ancient Egypt Established?
- Who were the ancient Egyptian Pharaohs?
- How many pharaohs were there in ancient Egypt?
- What was Egypt before it was Egypt?
- When Did Ancient Egypt Start and End?
- How Many Years Ago Did Ancient Egypt Start?
- What Empire Is Older Than Egypt?
- What Was Life Like in Ancient Egypt?
- What Did the Ancient Egyptians Believe?
- What Did Ancient Egyptians Eat and Drink?
- Ancient Egypt Map
- Conclusion
When Was Ancient Egypt Established?
3100 BCE is the date ancient Egypt was founded after Pharaoh Narmer (also called Menes) united Upper and Lower Egypt to begin the Early Dynastic Period. This unification provided the stage for centralized government, which promoted stability and, ultimately, prosperity. If you’ve wondered, "When did ancient Egypt start and end," the story begins with this pivotal moment.
Prior to this unification Egypt was divided into several independent, usually small, autonomous regions, known as nomes, which were in the charge of local leaders.
This early period was marked by a huge leap forward in writing, architecture, and governance. Hieroglyphics came into existence as a record-keeping form and monumental structures started to take shape, forecasting the later dynastic grandeur. These innovations laid the groundwork for answering the question, "When did ancient Egypt start and end?"
Who were the ancient Egyptian Pharaohs?
More than kings, Pharaohs, were regarded as living gods and acted as go-between the deities and their people. Each pharaoh had absolute power and it was the responsibility of each pharaoh to maintain Ma’at, the principle of cosmic order and harmony.
Pharaohs were also often associated with the god Horus, protector of the monarchy, and upon their death, those kings were associated with Osiris, the god of the afterlife.
Some of the more well-known pharaohs include Khufu, who commissioned the building and construction of the Great Pyramid of Giza; Hatshepsut, one of the few female pharaohs who also expanded trade and built great temples; and Ramses II, known for military victories and monumental architecture like Abu Simbel Temple.
These rulers embodied the civilization’s resilience, helping answer the recurring question, "When did ancient Egypt start and end?" through their monumental achievements and influence.
— Experience Egypt like you have never done before through our 10-day round Trip Nile Cruise and Pyramids. From the Pyramids of Giza to the treasures of Luxor, the Nile cruise is a sure way of experiencing the best of Egypt and taking a look at the 10 Days Cairo, Aswan, Luxor & Hurghada Overland Tour . Book your experience today!
Maybe like: What are the important holidays in Egypt ?
How many pharaohs were there in ancient Egypt?

Egypt was ruled by about 170 pharaohs over 30 dynasties over a period of 3,100 years. This number of Pharaohs ruled Egypt through the Early Dynastic Period, the Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom, the New Kingdom, and the Late Period.
Each dynasty referred to the period when a family or lineage ruled; some pharaohs reigned for decades, others for less than a few years. Examples included Pepi II, who reigned for more than 90 years, and others who reigned for surprisingly short times because of political instability and occasional external invasions. There are many pharaohs that are well documented, but there are also many of them that leave little evidence of what their reign contained.
This vast lineage of rulers, each with unique contributions, forms a key part of answering the question: “When did ancient Egypt start and end?”, providing a detailed glimpse into its long-lasting legacy.
What was Egypt before it was Egypt?

Before it would be the unified kingdom of Ancient Egypt, the region was home to a collection of independent communities and cultures around the Nile River called “nomes”. These early societies have been called pre-dynastic Egypt, between about 6210 and 3100 BCE, and were composed of small, agricultural settlements. These communities depended on the Nile for water, fertile soil, and transportation routes.
Over time, and around 4000 BCE, the Predynastic Period saw the emergence of two distinct regions: Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. These regions were culturally and politically different, with different rulers, as well as different religious practices and also different artistic styles.
Narmer combined these regions under his rule unifying them into one cohesive civilization around 3100 BCE. This answers “When did Ancient Egypt start and end” opening the door for centuries of cultural and political achievement.
— Travel and see the historical sites of Egypt as you take our 8 Days Cairo, Luxor, Aswan Classic Tours. Discover the glory of Egypt by visiting the Pyramids, taking the Nile cruise, and discovering Luxor and Aswan. So do not waste your time, Do not miss 8 Days Cairo to Abu Simbel and Back Overland see, book your fantastic journey now!
Read more: Strange Facts About The Pyramids
When Did Ancient Egypt Start and End?

The beginning of ancient Egypt occurred about 3100 BCE when Narmer united Upper and Lower Egypt making the beginning of the Early Dynastic Period, by which stage the political and cultural development had been achieved.
There was the decline of a civilization, which began during the Third Intermediate Period (1070–664 BCE) owing to invasions and internal conflicts. There was a brief resurgence in the Late Period, which lasted from 664–332 BCE until Egypt fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BCE. The last chapter of ancient Egypt history was 30 B.C.E. when the Roman Empire annexed Egypt on the death of Cleopatra VII.
How long did ancient Egypt last? Ancient Egypt timeline is nearly 3,000 years long and shows an amazing adaptability and endurance that makes it one of the most studied civilizations of its time.
— Looking for an exciting way to explore the Egyptian wonders? You should try Egypt Classic Tours ; book one today! Starting from Cairo’s Pyramids up to the Temples of Luxor and everything in between Egypt's History unfolds itself to you, I would like to say do not miss seeing our new museum in Egypt soon take a look at the Grand Egyptian Museum Trial Phase Tour . Reserve now!
How Many Years Ago Did Ancient Egypt Start?
When we try to put Ancient Egypt’s beginnings into context, it began around 5,100 years ago, or about 3100 BCE. It is therefore one of the first and longest-lived civilizations in human history.
In fact, Ancient Egypt timeline began almost 2,000 years before Ancient Greece surfaced and nearly 1000 years ahead of the construction of Stonehenge.
The Nile’s fertile banks guaranteed such longevity as did the stability of an agricultural system, cultural adaptability, and finally, a centralized government under pharaohs.
Reflecting on this timeline deepens our appreciation of the question, "When did ancient Egypt start and end," revealing a civilization of remarkable endurance and influence.
What Empire Is Older Than Egypt?
In fact, the Sumerian Empire in Mesopotamia is older than Ancient Egypt, even though Egypt is one of the world’s oldest civilizations. By about 4500 BCE, the Sumerians founded city-states such as Uruk many hundreds of years before Egypt’s unification in 3100 BCE.
Unlike Egypt’s unified kingdom, the Sumerian city-states were independently ruled by local rulers. Despite their differences, these civilizations played their role in early human development.
Summer is, indeed, older in some respects, but none of the ancient civilizations have ever achieved the kind of sustained impact and monumental achievements that Egypt did throughout its long history.
So, when did ancient Egypt start and end? It spans thousands of years, far surpassing Sumer’s influence.
Read more: Is The Sphinx Older Than The Pyramids
What Was Life Like in Ancient Egypt?
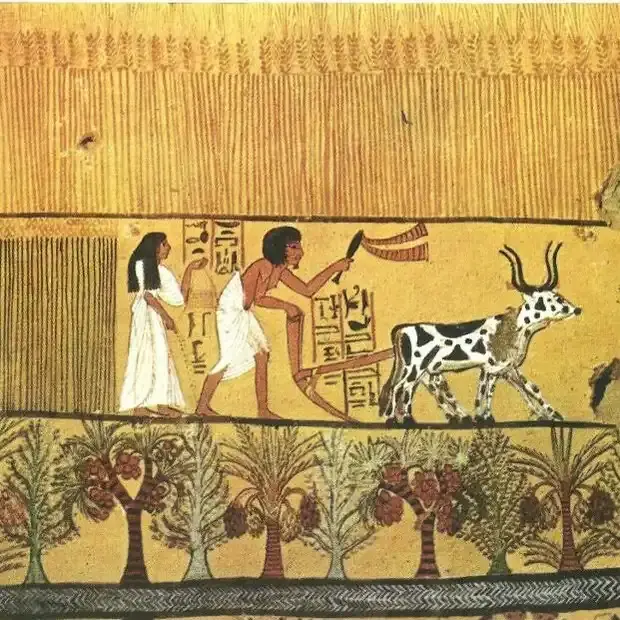

Life in Ancient Egypt focused on the Nile River for its water supply, food, and transportation. Most Egyptians were farmers growing crops such as wheat and barley; there were also craftsmen and merchants consisting of the middle class. Meanwhile, the upper class, which consisted of priests and officials, enjoyed more privileges and luxuries. Houses were built of mud bricks; the larger and more elaborate belonging to the affluent Egyptians.
Community life was replete with energy, including festivals, religious rituals, and creativity. Family life was highly respected by the Egyptians. Even within the very structured social classes, there existed a strong sense of community and religion that bound society.
When considering “when did ancient Egypt start and end”, it is important to note that these cultural practices and life aspects endured for over 3,000 years, continuing to impact society today.
— Discover Egypt’s history in a whole new way with the Egypt tour packages. Take tours to the Pyramids of Egypt, the world's longest river the Nile, and temples in Luxor, I would like to make you see our new packages 10 Days Round Trip Nile Cruise and Pyramids . Book now and try the original experience of ancient Egyptian history!
What Did the Ancient Egyptians Believe?

We will review below some aspects of the beliefs of ِAncient Egypt:
Polytheism
The ancient Egyptians had enormous numbers of deities and all of them had their own control over some part of life and nature. Among the most important gods are Ra, the sun god, Osiris - the god of the afterlife, Isis - the goddess of magic and motherhood, and Anubis.- the God of Funerary Rites and the Underworld . The gods can be considered mighty, but they needed people to perform sacrificial rites and to supply them with offerings in order to sustain the Ma’at: the balance of order and chaos in the world.
Pharaoh as a Divine Figure
The pharaoh was believed to be a god in existence and was responsible for preserving Ma'at. Pharaohs were supposed to act as intermediaries between the gods and the people.
The Afterlife
Egyptians had faith in existence after death, where the soul would pass into the Field of Reeds which is paradise. This belief influenced even how bodies were preserved through mummification and how tombs were constructed. This concept of rebirth connects to the broader understanding of the question of “When did ancient Egypt start and end”, as the belief in life after death played a central role throughout the civilization's history.
Judgment of the Dead
According to Egyptian mythology after death, a person’s heart was weighed against a feather of Ma’at by the god Anubis. A balanced heart allowed one to pass into the afterlife, while an imbalance brought the end by Ammit, the soul devourer.
Mummification
Mummification was highly connected with the beliefs which Egyptian people had regarding life after death. The body had to be preserved so that the soul could properly proceed on its journey. The body was then embalmed and offerings were made to the gods to ensure a safe journey.
Temples and Rituals
Temples were places of worship, religious ceremonies, and community gatherings. Each god had specific temples that were to be used by specific priests to perform rituals and offered food and gifts to nourish the god’s spirit.
Cosmology
The old Egyptians thought that life revolved in a cycle, and the daily movement of the sun, from dawn to dusk and back, was an indication of rebirth.
Ma’at and Cosmic Order
Indeed, everything in Egyptian society had a correlation with Ma’at which is the concept of order, truth, and justice. That is why, maintaining Ma’at was considered to ensure the prosperity of Egypt, and whenever Ma’at was disturbed, chaos ruled.
Festivals and Celebrations
The Opet Festival in Thebes is a clear example of the functionality of Religious festivals as a uniter of society and as a way to honor the gods. They included music, dancing, and processions.
Sacred Animals
Specific animals were sacred and were worshiped; for example, cats - as representatives of Bastet and crocodiles - as representatives of Sobek.
Magic and Amulets
Magic was an apparent part of Egyptian culture and tradition. Talismans and charms shield a person from potential dangers and also ensure the gods’ favor.
When reflecting on the question: When did ancient Egypt start and end, it’s clear that the Egyptian belief system was central to its long-standing success, shaping its social, cultural, and religious practices.
— Egypt Luxury Tours will show you the true wonders of Egypt. From the accommodation to guided tours, there is no moment where you do not feel like you are on a dream holiday. Experience ancient history, stunning landscapes, and opulent indulgence like never before. You need to have a good time with our 5 Days Cairo to Luxor Tour Packages
Read about: Did Thoth Built The Pyramids
What Did Ancient Egyptians Eat and Drink?
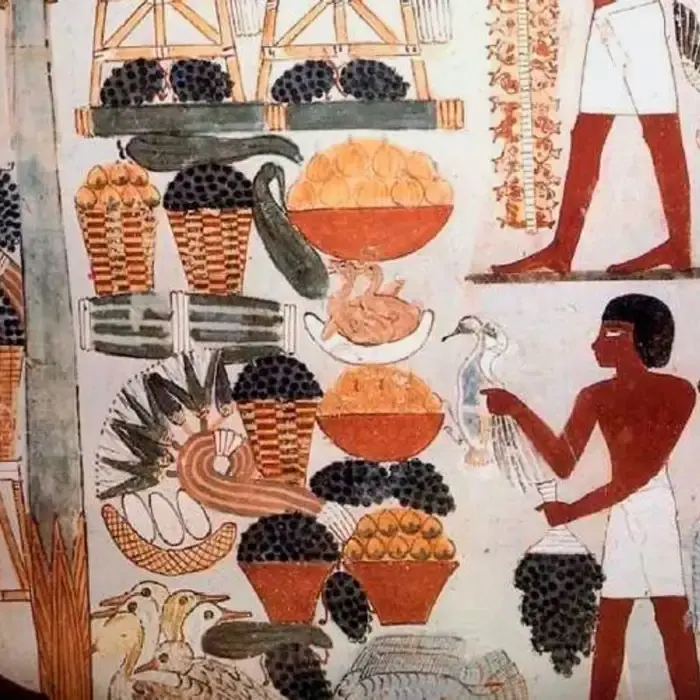

Staple Foods
Nile agricultural abundance was the principal source of the ancient Egyptians’ primary foods. Their daily diet was bread, usually made from wheat or barley, often together with beer. People of all social classes drank beer, which was made from fermented barley.
Vegetables and Legumes
Onions, garlic, leeks, lentils, and beans, all were part of the Egyptian diet. They were often used as a complement of staple foods, or made into soups and stews. Also, gardens grew cucumbers and lettuce that were consumed regularly.
Fruits
Some fruits, such as dates, figs, pomegranates, and grapes, were enjoyed by the Egyptians. They ate dates straight or made sweet treats out of them. Apples and melons, too, were part of the diet.
Meat and Fish
In Ancient Egypt, there was generally limited meat consumption; instead, it was eaten by the wealthy or at religious festivals. In fact, beef, goat, and sheep were eaten, but most of the public would have mainly depended on fish from the Nile such as catfish and tilapia, or poultry such as ducks and geese. The elite also often ate pigeons and quail.
Dairy Products
Although other foods are more common, the ancient Egyptians ate cheese, butter, and milk—mostly from cows and goats.
Seasonings and Oils
Herbs such as coriander and cumin were found to be used to flavor the food in Ancient Egypt. For cooking and dressing dishes, they used olive oil and sesame oil.
Sweets
Cakes and confections were sweetened most often with honey. Another alternative to sweetness was date syrup.
Beverages
Other than beer, wines were consumed particularly by the elites. Most of this wine was made from grapes and was used on spiritual occasions.
As we reflect on when ancient Egypt started and ended, it's fascinating how the Egyptian diet and the resources provided by the Nile played such an integral role in the daily life and sustenance of this enduring civilization.
Ancient Egypt Map
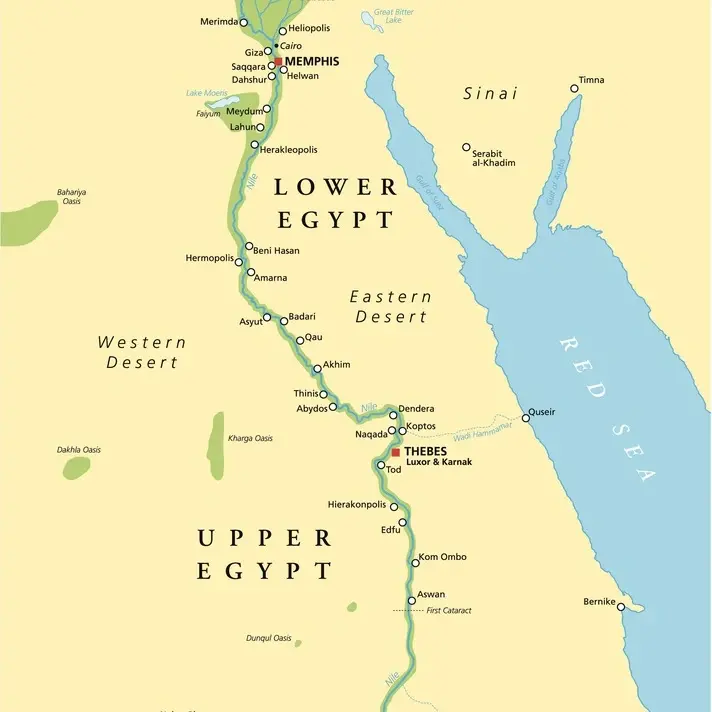
The Nile River took the central position on the map of Egypt and divided the country into two regions, Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. The result of this fertile area was that great cities like Memphis, the capital of Egypt’s Old Kingdom, and Thebes – a religious center and a political one as well – could be sustained. The Sahara and the Eastern Desert played the role of defensive walls protecting Egypt from invasions. More so, trade expanded its ways to Nubia and the Levant deepening its control.
Egypt enjoyed even more prosperity because there were economic exchanges through the Mediterranean and Red Sea. On such a basis, geography was very important to support Ancient Egypt’s prosperity in economic, cultural, and political aspects.
When did ancient Egypt start and end, geographically speaking, Egypt was a civilization defined by its fertile riverbanks and strategic location, allowing it to flourish for millennia.
Maybe like: Can You Go Inside The Great Pyramids
Conclusion
Ancient Egypt, lasting some 3000 years, is one of the most extraordinary civilizations to have occupied this world. Understanding "When did ancient Egypt start and end" provides invaluable insight into the achievements of this extraordinary civilization. Starting with Narmer who united Upper and Lower Egypt around 3100 BCE, it found its success through innovation, governance, and cultural advancements.
Although its decline set in 30 BCE when Rome annexed it, Ancient Egypt will never be forgotten. From the architectural wonders to spiritual groundwork Egypt has always richly contributed to humanity’s knowledge base.
Popular Categories
Popular Posts

Top Alexandria Beaches You Must Visit 2026

What are the important holidays in Egypt?








