Where is Memphis in Egypt? This ancient city near Mit Rahina was once the heart of a great civilization. Today, its ruins still tell stories of power and culture that shaped history. Did you know Egypt’s tourism grew by 50% in 2024? Egypt welcomed a record 15.7 million tourists that year, with more visitors seeking off-the-beaten-path sites like Memphis (Source: UNWTO.org) . Why does this city still matter after thousands of years? Let’s explore the 7 secrets of Egypt’s first capital.
Table of contents [Show]
- Discovering Memphis: Egypt's Ancient Capital
- Where is Memphis in Egypt?
- Surprising Facts About the History of Memphis City?
- Tips for Visiting Memphis
- Why was it called Memphis? 7 True Facts About the City's Name
- Rameses II: Giant Statues and Great History
-
The Open Museum in Meet Raheena: Where Memphis’s Ancient Heart Still Beats
- Why Visit the Open Museum in Mit Rahina?
- Quick Facts Table: Open Museum Highlights
- How the Open Museum Brings History Alive?
- Highlights of the Mit Rahina Open-Air Museum
- Key facts about Ramses II's statues in Memphis
- Why This Place Beats Competitors?
- Here is a table detailing the key archaeological highlights
- Key visitor information
- What Was Egypt’s First Capital? A Simple Guide to Its Name, History, and Role
- The Necropolis of Memphis: 10 Hidden Truths About Egypt’s City of the Dead (And How to Explore It)
- Where Is Memphis in Egypt on a Map? Find the Ancient Capital’s Exact Location
- Who built the city of Memphis, Egypt?
- Why Was Memphis Built? A Clear Look at Egypt’s First Capital
- Memphis Egypt Facts: Surprising Truths About the Ancient World’s First Supercity
- What is Memphis, Egypt, famous for?
- What Is There To See In Memphis, Egypt?
- Is Memphis Egypt Worth Visiting? Here’s Why This Ancient City Still Matters Today
- How to Get Around Memphis, Egypt: Simple Tips for Easy Travel Near Cairo’s Oldest Capital
- Features & importance of Memphis Ancient Egypt
- Ancient City of Memphis Museum: A Window into Egypt’s Past
- Memphis Egypt as a World Heritage Site: Why It Earned Global Recognition and Still Deserves a Visit Today
- Why Was Memphis, Egypt, Abandoned? Key Reasons Behind the Ancient City’s Decline
- The Summary
Discovering Memphis: Egypt's Ancient Capital
Memphis was once Egypt's shining capital. Even today, its ruins whisper tales of pharaohs and gods. Where is Memphis in Egypt? Journey with us to discover its location and what made it so vital.
Where is Memphis in Egypt?
- Situated on the west bank of the Nile River, marking the boundary between Upper and Lower Egypt.
- You'll find it about 24 kilometers (15 miles) south of Cairo.
- The ruins are near Mit Rahina, a modern Egyptian village.
- Memphis sits roughly 3 kilometers from Saqqara.
- Its strategic spot was at the meeting of Upper and Lower Egypt.
Quick Facts About Memphis' Location
Fact | Details |
Near Cairo | About 24 km (15 miles) south |
Nile River | West bank, south of the Delta |
Modern Village | Close to Mit Rahina |
Other Ancient Sites | 3 km from Saqqara |
Why Memphis' Location Mattered
- The location boosted trade and commerce.
- It gave access to both Upper and Lower Egypt.
- Memphis controlled the Nile Delta entrance.
- Its port had workshops and warehouses for goods.
- Being near the Nile allowed easy transport.
Memphis' location shaped its story. From trade hub to royal capital, its place on the Nile made it great. When you visit, remember where it all began. The city's legacy lives on—and it's now featured among the best cities to visit in Egypt 2025
Surprising Facts About the History of Memphis City?
Memphis, Egypt, lies about 20 kilometers south of Cairo near the village of Mit Rahina. Where is Memphis in Egypt? This city was the center of political power and religious life in ancient Egypt. Knowing where Memphis is in Egypt reveals why it was so important—and connects directly to these facts about ancient pyramids in Egypt.
Memphis, Egypt: The Ancient Capital Where Egypt’s Story Began
Memphis shaped Egypt’s history for centuries, from the rise of the first pharaohs to the building of pyramids and temples. Today, its ruins tell a story that goes beyond the famous pyramids of Giza.
A Quick Look at Memphis’s Early Days
- Founded around 3100 BCE by King Menes, the first ruler to unite Upper and Lower Egypt into one kingdom.
- Originally called Ineb Hedj or White Walls, probably named after the whitewashed palace walls.
Before its decline, Memphis held several important names. Here is a table detailing them:
Ancient Name | Meaning | Significance |
Ineb Hedj | The White Walls | Original name, likely referring to the royal palace |
Men-nefer | Enduring and Beautiful | The name of Pepi I's pyramid became the Greek Memphis |
Ankh Tawy | That which binds the Two Lands | Reflected its strategic location between Upper and Lower Egypt |
Hut-ka-Ptah | Mansion of the Ka of Ptah | Referred to as the Great Temple of Ptah, later became Aigyptos (Egypt) |
- Strategically located on the west bank of the Nile, just south of the Nile Delta, perfect for trade and control.
- Memphis held control over major trade routes between Egypt’s north and south.
Key Fact | Detail | Why It Matters |
Founder | King Menes (Narmer) | United Egypt under one rule |
Location | Near Mit Rahina, 20 km south of Cairo | Control over the Nile trade routes |
Original Name | Ineb Hedj (“White Walls”) | Symbol of royal power |
Capital Era | Old Kingdom (2686–2181 BCE) | Height of the pyramid building |
Religious Center | Temple of Ptah | Worship of the craftsman god Ptah |
Memphis in Its Prime: The Old Kingdom Era
Under the Old Kingdom, Memphis was unquestionably Egypt's capital.
Pharaoh Djoser, famous for the Step Pyramid at nearby Saqqara, made Memphis a cultural and political hub.
The Great Temple of Ptah in Memphis was a religious powerhouse, dedicated to the god of craftsmen and architects.
Memphis was a hub for culture, religion, business, and politics.
Pharaohs lived, ruled, and planned their eternal monuments here.

Memphis Through Time: Middle and New Kingdoms
- It maintained its significance as a political and religious hub even after the capital was relocated during the Middle Kingdom.
- It was the capital of the North under the New Kingdom and occasionally the residence of crown princes.
- Famous pharaoh Ramses II brought new life to Memphis with colossal statues, many of which still stand or lie on display.
- Each king of the 18th dynasty added to the Temple of Ptah, keeping Memphis’s spiritual power alive.
The Slow Fade and Lasting Legacy
Memphis’s decline started as Alexandria rose under the Ptolemies. Christianity’s spread reduced temple visits, and by the Islamic period, Memphis was mostly ruins. Stones from its temples were repurposed to build Cairo.
Yet Memphis’s story endures. It’s a UNESCO World Heritage Site, preserving a glimpse into Egypt’s powerful past.
Religion at Memphis: The Cult of Ptah
- Ptah was the creator god and patron of builders, central to Memphis’s identity.
- Worshippers believed Ptah created the world by thought and speech.
- Ptah, his wife Sekhmet, and their son Nefertem made up the Memphite Triad, and they were extremely important spiritually.
- The Apis bull cult, representing a living form of Ptah, was unique to Memphis, with the bulls mummified and honored in the nearby Serapeum at Saqqara.
What’s Left to See Today?
Memphis today is an open-air museum with ruins near Mit Rahina.
Site | Description |
Ramses II Statue | Massive statue lying on its back (~10 m) |
Alabaster Sphinx | 26-foot-long sphinx carved from one block |
Temple Remains | Columns and foundations of temples |
Necropolis of Saqqara | Burial grounds with the Step Pyramid and more |
Tips for Visiting Memphis
- It’s about 20 km south of Cairo, reachable by taxi or tour.
- To avoid the heat and crowds, it is best to go early
- Combine your trip with Saqqara and Giza for a full experience.
- Wear comfortable shoes; the site is uneven and sandy.
- Hire expert guides like Egypt Online Tour guides for a richer visit.
- Learn more about: Tips on traveling to Egypt
Why Memphis Deserves Your Visit
- Most tourists rush to Giza and miss Memphis, the city that set the foundation for all Egyptian greatness.
- Walking through Memphis’ ruins is stepping into the real origin of pharaohs, pyramids, and religion.
- The quiet grounds offer a peaceful, thoughtful experience without the tourist crush.
Learn more about: Egypt trips to the pyramids
Key Figures in Memphis's History
Many rulers left their mark on Memphis. They shaped its destiny and added to its grandeur.
Pharaoh/Figure | Dynasty/Period | Connection to Memphis |
Menes (Narmer) | Early Dynastic | Founded the city; united Upper and Lower Egypt. |
Djoser | Old Kingdom (3rd) | Solidified Memphis as capital; his Step Pyramid was built nearby. |
Pepi I | Old Kingdom (6th) | His pyramid, Men-nefer, gave Memphis its Greek name. |
Ramses II | New Kingdom (19th) | Revitalized the city; commissioned colossal statues. |
Amenhotep II | New Kingdom (18th) | Born in Memphis, served as high priest there. |
Thutmose IV | New Kingdom (18th) | Had strong ties to the city; left inscriptions at Giza. |
Akhenaton | New Kingdom (18th) | Built a temple to his god, Aten, within Memphis. |
Hyksos (Salitis) | Second Intermediate | Historical accounts suggest he may have made Memphis his capital. |
Piye & Taharqa | Late Period (Nubian) | Nubian kings who conquered Egypt; Piye besieged Memphis. |
Alexander the Great | Ptolemaic Period | His body was temporarily laid to rest in Memphis. |
Ready to explore the roots of Egypt? Book your Memphis visit now with Egypt Online Tour
Memphis is not just stones in the sand. It’s the cradle of Egypt’s unity and power. Its “White Walls” witnessed the birth of a kingdom and the building of timeless monuments.
Though time has buried much, Memphis’s spirit remains alive in every statue, temple remnant, and story. If you’ve ever asked Where is Memphis in Egypt, the answer leads you to a place that shaped a civilization. Visiting Memphis reveals the real heartbeat of ancient Egypt — the foundation on which all else was built. It’s also a key to understanding What are 3 major achievements of ancient Egypt?.

Why was it called Memphis? 7 True Facts About the City's Name
Wondering where is Memphis in Egypt and how it got this famous name? You're not alone. The answer mixes pharaoh pride, lost languages, and a Greek translation.
Quick History: How Memphis Got Its Name
- Original Egyptian Name: It was first called Ineb Hedj, meaning White Walls.
- Why That Name? Bright white palace walls could be seen from far away. It showed royal strength.
- Second Name: Enduring and Beautiful (Men-nefer). Later, the city took on this name.
- It came from the pyramid of King Pepi. This pyramid was called Men-nefer.
- Greek Influence: Greeks couldn’t pronounce Men-nefer, so they said Memphis.
- Cultural Shift: As Greek and Roman writers traveled, they used “Memphis” in their texts.
- Why It Stuck: The Greek version became the common name in history books.
Today, we still say Memphis, even though Egyptians never used that word.
Name: Evolution of Memphis
Period | Name | Meaning | Origin |
3100 BCE | Ineb Hedj | The White Walls | Egyptian palace architecture |
2300 BCE | Men-nefer | Enduring and Beautiful | Pepi I’s pyramid complex |
500 BCE (Greek) | Memphis | Greek version of Men-nefer | Greek historical texts |
Today | Memphis / Mit Rahina | Modern village | Holds the ruins of the ancient city |
Why the Name Memphis Mattered
- Royal Message: Ineb Hedj warned outsiders—this was Pharaoh territory.
- Religious Connection: This location was used to worship the god of creation, Ptah.
- Political Branding: Using Men-nefer linked the city to Pharaoh Pepi I’s glory.
- Language Shift: Greeks wrote about Egypt, so their version became dominant.
- Enduring Legacy: Even when the city fell, the name Memphis stayed in global memory.
Fun Facts About the Name Memphis
- The name “Memphis” was later reused in Tennessee, USA.
- Ancient Egyptians didn’t use vowels in writing, so meanings changed over time.
- Memphis also appears in biblical texts under names like Moph or Noph.
- Mit Rahina is the modern village where the ruins still lie.
So, why was it called Memphis? Because names change, but meaning survives. From “White Walls” to “Enduring and Beautiful” to “Memphis,” this city’s title reflects its history. Next time you wonder where is Memphis in Egypt, remember, it’s not just a place. The story has been etched in stone for 5,000 years.
Explore it yourself with Egypt Online Tour—start with this guide on how to plan a family vacation in Egypt from USA.
Rameses II: Giant Statues and Great History
Ramses II ruled Egypt for over six decades. His giant statues still stand as bold symbols of his power and reign. Near Memphis, these massive works tell stories of strength, faith, and leadership. If you wonder where is Memphis in Egypt, it lies close to Cairo, where its legacy lives on.
Key Facts About Ramses II’s Giant Statues
- Long Rule: Ramses II was Egypt’s pharaoh for 66 years, shaping much of its history.
- Master Builder: Rameses II built many temples and monuments across Egypt, leaving a lasting mark.
- Famous Colossus at Memphis: Near the ancient city, a 33-foot limestone statue lies on its back, likely toppled by earthquakes.
- Abu Simbel Temples: Two rock temples honor Ramses and Queen Nefertari. In order to prevent floods, In order to prevent floods, they were relocated in the 1960s.
- Luxor Statues: Large statues once flanked his temple; only one remains after earthquake damage.
- Ancient Photoshop: Ramses sometimes carved his face on older statues to claim power.
- Military Leader: His battles, especially Kadesh, are carved in stone on his monuments.
- Religious Symbol: Many temples and statues show Ramses as a god-like ruler, linked to Egypt’s gods.
- Artistic Skill: The statues show the high craftsmanship of ancient Egyptian artists.
- Memphis Connection: Ramses’s statues guarded and glorified the city when it was Egypt’s key center.
- Tourist Highlights: Visitors today come to see these statues and learn about Ramses’s influence.
- Preservation: Experts work to protect these giant statues from weather and damage.
- Cultural Impact: Ramses’s statues inspire stories, films, and admiration worldwide.
- Family Man: Had over 100 children and many wives, making his family huge and influential.

Ramses II Statues at a Glance
Location | Statue/Monument | Size (Feet) | Material | Why It Matters |
Memphis (Mit Rahina) | Fallen Colossus | 33 | Limestone | Symbol of reign strength, still admired |
Abu Simbel | Twin Rock Temples | 65 | Sandstone | Engineering marvel, saved from floods |
Luxor | Seated Statue | 57 | Granite | Surviving statue from the grand temple |
Tanis | Reused Colossal Statues | 28 | Granite | Shows Ramses’s power claims |
Why Ramses II’s Statues Still Matter
- Draw Millions: Abu Simbel is one of Egypt’s top tourist sites.
- Historic Records: The triumphs and family of Ramses are shown in statues and temples
- Symbol of Egypt: Locals see Ramses as a sign of their country’s rich past.
- Inspiration: His image is famous in books, movies, and culture worldwide.
- Living History: Visiting these statues connects us directly to ancient Egypt’s glory.
Why Most Tours Miss the Real Story?
- Focus Only on Dates: They list dates without stories.
- Crowded Visits: Tourists rush in at noon, missing quiet mornings.
- Skip Hidden Gems: Few see his reused statues in Tanis or know his “ancient edits.”
Ramses II’s statues are more than stone—they are echoes of a king’s life. To experience the essence of ancient Egypt, visit them.
Visit Now: Explore Ramses II’s Statues with Egypt Online Tour
Read about: How many wives did King Ramses II have
The Open Museum in Meet Raheena: Where Memphis’s Ancient Heart Still Beats
The Open Museum in Mit Rahina offers a rare chance to see history under the open sky. Located near the ancient city of Memphis, it holds treasures that tell stories of Egypt’s past. If you wonder where is Memphis in Egypt, this museum is a must-visit. You can also pair it with the Grand Egyptian Museum tour to deepen your journey into Egypt’s heritage. Below, discover why this open-air museum is a hidden gem for history lovers and travelers alike.
Why Visit the Open Museum in Mit Rahina?
- Outdoor Experience: Unlike closed museums, here you walk among giant statues and ruins in the fresh air.
- Giant Statues: See massive statues of pharaohs, including a famous fallen statue of Ramses II.
- Ancient Artifacts: The site displays stone blocks, temple fragments, and old inscriptions.
- Peaceful Setting: The open space gives visitors room to explore without crowds.
- Educational Signs: Clear explanations help you understand the history behind each artifact.
- Easy Access: Located about 20 km south of Cairo, it’s a short trip from the city.
- Photographer’s Delight: The natural light and open sky make it perfect for photos.
- Connection to History: Walking here feels like stepping back into Egypt’s golden age.
- Less Touristy: Fewer visitors than Giza, so you get a more personal experience.
- Budget-Friendly: Tickets cost less than a fancy coffee. Bonus: Kids under 6 get in free.
Learn more about: How to Plan a Trip to Cairo Egypt
Quick Facts Table: Open Museum Highlights
Feature | Details | Why It Matters |
Location | Near Mit Rahina village, south of Cairo | Close to ancient Memphis ruins |
Main Attractions | Fallen Ramses II statue, temple blocks | Showcases royal power and craftsmanship |
Museum Type | Open-air, outdoor exhibits | Unique way to experience ancient Egypt |
Visitor Tips | Visit early morning or late afternoon | Avoid heat and crowds |
Accessibility | Easy road access from Cairo | Suitable for day trips |
How the Open Museum Brings History Alive?
- Feel the Scale: Egypt's monarchs' stature and strength are depicted by the enormous statues.
- See the Details: Close-up views reveal fine carvings and ancient artistry.
- Walk the Grounds: Explore temple ruins and imagine the bustling city that once stood here.
- Learn on Site: Informative plaques guide you through Egypt’s early history.
- Experience the Past: The open sky and natural surroundings add to the magic.
Highlights of the Mit Rahina Open-Air Museum
- Colossal Statue of Ramses II: A 10-meter-long limestone statue, discovered in 1820, lies majestically within a protective enclosure.
- Alabaster Sphinx: Weighing over 80 tons, this sphinx is carved from a single piece of alabaster, reflecting the artistry of the New Kingdom.
- Temple of Ptah Remnants: Explore the ruins dedicated to Ptah, the creator god, which once stood as a significant religious center.
- Ancient Artifacts: The museum houses various statues, stelae, and architectural elements from different periods of Egyptian history.
- Historical Significance: The site provides insights into Memphis's role as a political and cultural hub in ancient times.
Key facts about Ramses II's statues in Memphis
Feature | Detail | Significance |
Location | Mit Rahina Open-Air Museum, Memphis | The main modern site to see this iconic statue |
Size | Approximately 10 meters (33 feet) tall | Shows the pharaoh's immense power and status |
Material | Carved from a single block of limestone | Highlights incredible ancient Egyptian artistry |
Original Purpose | Stood at a temple entrance, likely Ptah's temple | Symbolized divine authority and royal presence |
Current State | Lies horizontally under a protective roof | Still a major attraction despite its fallen state |
Ramses II's giant statues in Memphis are more than just old stones. They are a direct link to a powerful pharaoh. They tell a story of ambition, artistry, and lasting influence. Seeing them helps you feel the grandeur of ancient Egypt. If you’ve ever wondered where Memphis is in Egypt, this is the place to find the answer. It is a truly unforgettable experience.
Why This Place Beats Competitors?
1. No Crowds: Giza’s packed. Here, you can hear desert winds whisper.
2. Local Vibe: Guides crack jokes (Ramses’ ego broke the statue).
3. Real History: Walk where pharaohs actually ruled, not just tomb spots.
4. Photo Ops: Pose beside Ramses’ sandal. Yes, it’s taller than you.
Here is a table detailing the key archaeological highlights
Site/Monument | Location (within Memphis/Necropolis) | Description | Significance |
Mit Rahina Open-Air Museum | Ancient Memphis city site | Displays excavated artifacts and sculptures | The main modern site for exploring Memphis's remnants |
Colossal Statue of Ramses II | Mit Rahina Open-Air Museum | 10-meter (33-foot) limestone statue of the pharaoh | Symbol of royal power, artistic mastery, once adorned the Ptah Temple |
Alabaster Sphinx | Mit Rahina Open-Air Museum | Large alabaster statue combining human and lion forms | Testament to Egyptian artistry, cultural heritage |
Great Temple of Ptah (remnants) | Ancient Memphis city site | Foundations and scattered elements of the main temple | The center of Ptah worship, a vital religious hub |
Giza Necropolis | Northern Memphite Necropolis | Pyramids of Khufu, Khafre, Menkaure, and the Great Sphinx | Iconic Wonders of the World, royal burial grounds |
Saqqara Necropolis | Central Memphite Necropolis | Step Pyramid of Djoser, numerous mastabas, Serapeum | World's first stone pyramid, vast ancient cemetery |
Dahshur Necropolis | Southern Memphite Necropolis | Bent Pyramid, Red Pyramid (Pharaoh Snefru) | Evolutionary examples of pyramid construction, fewer crowds |
Heit al-Ghurab | Giza Plateau (within the Necropolis) | An ancient village for pyramid builders and craftsmen | Provides insight into the daily life of ordinary Egyptians |
Key visitor information
Item | Detail |
Adult Ticket Price (Other Nationalities) | EGP 200 |
Student Ticket Price (Other Nationalities) | EGP 100 (with valid ID) |
Children under 6 | Free entry |
Summer Working Hours | 08:00 AM - 04:00 PM |
Winter Working Hours | 08:00 AM - 04:00 PM |
Ramadan Working Hours | 09:00 AM - 03:00 PM |
Open Days | All Days |
What Was Egypt’s First Capital? A Simple Guide to Its Name, History, and Role
Egypt’s long story begins with one powerful city—its very first capital. Wondering where is Memphis in Egypt? This ancient place once ruled the land. Below, find facts that answer your question
What Was Egypt’s First Capital?
- Memphis was the First Capital: Founded around 3100 BCE by King Menes (Narmer), who united Upper and Lower Egypt.
- Geographic Advantage: Placed at the meeting point of Upper and Lower Egypt.
- Trade Access: Close to the Nile, Memphis controlled shipping routes.
- Religious Role: Home to the Temple of Ptah, Egypt’s creator god.
- Cultural Role: A center for arts, politics, and science.
- Political Center: Memphis served as Egypt’s political hub for over 800 years during the Old Kingdom.
- Name Evolution: “Memphis” comes from Men-nefer, a nearby pyramid complex of Pepi I.
- Greek Influence: Greek writers used “Memphis,” and that version lasted.
- Architectural Marvels: Known for colossal statues, temples, and the nearby necropolis of Saqqara with the Step Pyramid.
- Famous Statue: Ramses II’s 33-foot statue rests here.
- Saqqara Is Close: The world’s first stone pyramid stands just 3 km away.
- UNESCO Status: Memphis and its necropolis are protected heritage sites.
- Name Meaning: “Men-nefer” means “Enduring and Beautiful.”
- Biblical Mentions: Known as Moph or Noph in ancient texts.
- Decline: Lost importance after Thebes and later Alexandria rose.
- Still Important: Its history shaped Egypt’s government and religion.
- Modern Site: Mit Rahina gives visitors a direct view into Egypt’s origins.

Timeline of Memphis as Egypt’s Capital
Period | Event | Importance |
c. 3100 BCE | Founded by King Menes (Narmer) | Unification of Egypt |
Old Kingdom | Memphis as a political and religious center | The era of pyramid building and culture |
Middle Kingdom | Continued importance | Stability and growth |
New Kingdom | Decline begins as Thebes rises | Shift of political power |
Modern Era | Archaeological excavations begin | Rediscovery and preservation |
Why Memphis Was Egypt’s First Capital
- Strategic Location: Controlled movement between Upper and Lower Egypt.
- Religious Center: Ptah’s worship began here and spread across Egypt.
- Economic Power: Positioned perfectly to dominate trade along the Nile.
- Long Reign: Stayed the capital for over 800 years.
- Linked to Kings: Home to royal palaces and temples.
- Cultural Anchor: Many ideas that shaped Egypt started here.
Tips for Visiting What’s Left of Memphis
- Go Early: Avoid the midday heat.
- Bring Water: It’s an open-air site.
- Wear Shoes: Uneven stones make sandals risky.
- Hire a Guide: Locals tell stories you won’t find online.
- Combine Trips: See Saqqara or Dahshur on the same day.
Memphis wasn’t just Egypt’s first capital—it was where the nation began. Its story shows how location, leadership, and belief built one of the world’s earliest empires. Though time changed its role, the ruins at Mit Rahina still echo with that early greatness. If you’re asking where Memphis is in Egypt, you’re really asking: Where did Egypt begin?
Want more?
Visit the site with Egypt Online Tour and walk through the city that started it all.
The Necropolis of Memphis: 10 Hidden Truths About Egypt’s City of the Dead (And How to Explore It)
Just south of Cairo (where is Memphis in Egypt? Think 12 miles), Saqqara’s dusty plains guard Memphis’s afterlife secrets. Forget Giza—this sprawling necropolis hides wilder tales. Let’s crack them open.
- Creation of the pyramid: Imhotep constructed the Step Pyramid here first. Fun fact: It’s like a wedding cake for Pharaoh Djoser’s eternity party.
- Tomb trickery: Elite graves had decoy chambers. But here’s the twist—some had fake doors to trick tomb raiders..
- Hieroglyphic comic strips: Walls show farmers brewing beer, dancers mid-twirl, and even a monkey stealing snacks. Time travel, anyone?
- Mummified pets galore: Cats, dogs, and ibises buried by the millions. Locals believed they carried prayers straight to the gods.
- The Doctor’s Tomb: Found surgical tools, prescriptions etched on walls. One remedy? Honey mixed with garlic for infections.
- Secret tunnels: Looters dug miles under Saqqara. Archaeologists later found mummies, gold, and a 4,400-year-old cheese stash.
- Bull-sized burials: Apis bulls got 80-ton coffins. Workers likely slid them on reed sleds drenched in Nile water. Genius.
- Curse of the Pharaohs? After Tut’s tomb made headlines, Saqqara workers blamed headaches on angry spirits. Spoiler: It was dehydration.
- Rediscovery drama: A German tourist tripped over a stone in 2018. Turned out to be a priest’s tomb packed with art.
- New digs, fresh finds: In 2023, a hidden shaft coughed up 250 painted coffins. Saqqara’s still got stories to spill.

Saqqara vs. Other Necropolises
Feature | Saqqara | Giza | Valley of the Kings |
Earliest pyramid | Step Pyramid (~2650 BCE) | Great Pyramid (~2560 BCE) | N/A |
Burial vibe | Mix of experiments & tradition | Perfect precision | Hidden, treasure-filled |
Mummy madness | Humans + millions of animals | Pharaohs & elites | Royalty only (no pets allowed) |
Art quirks | Beer-making, dance fails, and gods | Cosmic order & rituals | Divine kingship & underworld |
Crowds | Chill, more goats than people | Selfie armies by noon | Guided groups only |
Vibe check | Unpolished, raw history | Iconic but crowded | Mysterious but pricey |
Saqqara isn’t just Memphis’s graveyard—it’s a time capsule of chaos, art, and humanity. Unlike Giza’s postcard perfection, here, you’ll feel Egypt’s pulse. And if you’re asking where is Memphis in Egypt, Saqqara sits right next to it—quietly guarding the stories pharaohs left behind.
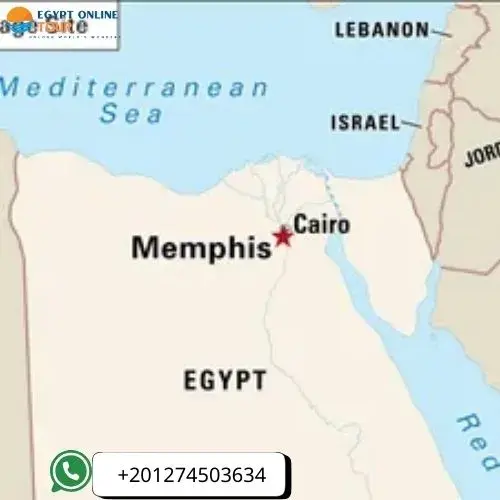
Where Is Memphis in Egypt on a Map? Find the Ancient Capital’s Exact Location
Memphis was Egypt’s first great capital. Today, its ruins lie near the small village of Mit Rahina. This location is on the west bank of the Nile River, some 20 kilometers (12 miles) south of Cairo. If you wonder where Memphis is in Egypt, here is a clear, simple guide to find it easily on any map.
- Memphis is located in the Giza Governorate, next to the village of Mit Rahina, just south of Cairo.
- Nile River: The city rests on the Nile’s west bank, marking the boundary of Upper and Lower Egypt.
- Nearby Landmarks: Close to Saqqara and Dahshur pyramids, making it a rich archaeological area.
- Coordinates: Approximately 29°50′41″N latitude and 31°15′3″E longitude.
- Contemporary Location: Memphis's ruins are shown in the open air at the Mit Rahina Museum.
- Strategic Location: Memphis used to be in charge of politics and trade in ancient Egypt.
- Easy Access: About 12 miles from Cairo, reachable by car or taxi within an hour.
- Quiet Surroundings: Less crowded than Giza, offering a peaceful visit to history lovers.
- Map Tips: Search Mit Rahina or Memphis, Egypt on Google Maps for precise directions.
- Historical Importance: Memphis was the heart of Egypt’s early civilization and commerce.
Knowing exactly where Memphis is helps you plan your visit and connect with Egypt’s ancient roots. Walk where pharaohs once ruled and explore a city that shaped history.
Who built the city of Memphis, Egypt?
King Menes constructed Memphis in 3100 BCE. He united Upper and Lower Egypt and chose the site for its central location. It stood on the Nile’s west bank, making trade and defense easier. Menes called it “White Walls.” Later, Greeks named it Memphis. It became Egypt’s first capital. If you wonder where is Memphis in Egypt, it lies near Mit Rahina, just south of Cairo, close to Saqqara and Dahshur.
Why Was Memphis Built? A Clear Look at Egypt’s First Capital
Memphis was built with a clear purpose: to unite, govern, and connect ancient Egypt. Here’s why this city became so important, told simply and clearly.
- Founded to Unite Egypt: Memphis was established around 3100 BCE by King Menes, who united Upper and Lower Egypt into one kingdom.
- Strategic Location: It sits at the mouth of the Nile Delta, on the west bank of the Nile, where Upper and Lower Egypt meet. This spot was perfect for control and trade.
- Political Capital: Memphis served as the first political and administrative center of the unified kingdom, managing resources and power.
- Religious Center: The city was home to the great temple of Ptah, the creator god, making it the spiritual heart of Egypt.
- Economic Hub: Its location allowed easy access to trade routes along the Nile and beyond, boosting Egypt’s wealth.
- Cultural Importance: Memphis became a place for artisans, scholars, and priests, nurturing Egypt’s early culture and traditions.
- Symbol of Stability: Building Memphis symbolized the strength and unity of the new kingdom, with “White Walls” representing protection and permanence.
- Legacy of Kings: Pharaohs of the Early Dynastic and Old Kingdom periods ruled from Memphis, building temples, palaces, and pyramids nearby.
- Long-lasting Influence: Even after losing its capital status, Memphis remained a key religious and commercial center for centuries.
Memphis was built to be the heart of a new Egypt — a place where power, faith, and culture came together. Knowing where Memphis is in Egypt helps you appreciate why this city mattered so much.
Memphis Egypt Facts: Surprising Truths About the Ancient World’s First Supercity
Memphis was a major city in ancient Egypt’s story. Its story is rich, and its ruins still speak volumes. Here are clear, simple facts about Memphis that bring history alive.
- Founded around 3100 BCE, Memphis was built by King Menes (Narmer), who united Upper and Lower Egypt.
- Original Names: Known as Ineb-Hedj (White Walls) and Hut-ka-Ptah (Enclosure of the Ka of Ptah), the city’s names reflect its power and religion.
- Capital for Centuries: It served as Egypt’s capital during the Early Dynastic Period and Old Kingdom, shaping the nation’s early politics.
- Mummy lab**: Priests here wrote the embalming playbook. Saqqara’s Step Pyramid? Their masterpiece’s backyard.
- Economic Hub: Its location on the Nile’s west bank made it a key trade and transport center.
- Famous Structures: The city held grand palaces, temples, and huge statues, including those of Ramses II.
- Cultural Crossroads: Traders, artists, and priests from all over Egypt and beyond gathered here.
- Decline and Legacy: Though it lost capital status to Thebes and Alexandria, Memphis remained influential for centuries.
- Modern Site: Today, its ruins lie near Mit Rahina village, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Known as “Ineb Hedj” or “White Walls” in early times, later named Memphis. Greeks loved it, locals built it, and everyone copied it.
- Pharaoh’s Seat: Many early pharaohs ruled from Memphis, building Egypt’s first great monuments.
- Center of Power: Memphis symbolized the unity of Egypt’s two lands and its early strength.
Memphis’s story is the story of Egypt’s rise. Knowing where is Memphis in Egypt helps you connect with this ancient heartbeat. The city’s ruins invite you to walk where history was made.
What is Memphis, Egypt, famous for?
Memphis, Egypt, is steeped in ancient wonders. What is Memphis, Egypt, famous for, you ask? This old city truly shaped a civilization. It holds secrets of pharaohs, gods, and grand beginnings. So, let’s dig into its lasting fame.
- First Capital, First Power: Memphis was Egypt’s very first capital. Therefore, it started a unified nation.
- Birthplace of Pyramids: The Step Pyramid of Djoser stands nearby. It’s the world’s oldest large stone building. Consequently, this site taught builders new tricks.
- Home of Ptah: Ptah, the creator god, lived here. His grand temple drew people far and wide. Thus, it was a spiritual hotspot.
- Colossal Statues: Giant statues of pharaohs, like Ramses II, still impress. They show ancient royal power. Indeed, they once guarded grand gates.
- Trade Hub: Memphis controlled the Nile trade routes. It was a bustling ancient marketplace. Therefore, wealth flowed through its docks.
- Royal Necropolis: Saqqara, a huge burial ground, served Memphis. Kings and nobles rest there. So, it holds many ancient secrets.
Memphis isn't just a place. It's where Egypt's amazing story began. And if you’ve ever asked where is Memphis in Egypt, it’s just south of Cairo, near Mit Rahina—still echoing with the legacy of kings.
What Is There To See In Memphis, Egypt?
What Is There To See In Memphis, Egypt? Discover the Ancient City’s Treasures
Memphis, Egypt, holds a wealth of history and stunning ruins. If you wonder where is Memphis in Egypt and what to explore, here’s a simple guide to its must-see sights. These highlights offer a glimpse into Egypt’s first capital and its lasting legacy.
- Colossal Ramses II Statue: This giant statue lies in the open-air museum at Mit Rahina. It’s a striking reminder of royal power.
- Temple of Ptah: This temple, which revered the goddess of crafts and creativity, was once the heart of Memphis' spiritual life..
- Ancient Ruins: Walk among the remains of palaces, temples, and city walls that tell stories of a mighty civilization.
- See sculptures and relics unearthed from the site at the Mit Rahina Museum, which is free to the public.
- Nearby Pyramid Fields: Saqqara and Dahshur pyramids are just a short drive away, perfect for day trips.
- Nile River Views: Enjoy the scenic Nile banks, which once fueled Memphis’s trade and agriculture.
- Historic Necropolis: Explore the burial grounds where pharaohs and nobles were laid to rest.
- Cultural Legacy: The site reflects Egypt’s early unity and religious traditions, still felt today.
- Quiet Atmosphere: Unlike crowded tourist spots, Memphis offers a peaceful, reflective visit.
- Easy Access: Located near Cairo, it’s an ideal stop for history lovers exploring Egypt.
Memphis welcomes you to travel back in time and discover the origins of Egyptian culture.. Knowing where Memphis is in Egypt helps you plan a meaningful visit to this ancient city.
Learn more: Is Cairo safe for American tourists
Memphis's key attractions:
Attraction | Description | Significance |
Colossal Ramses II Statue | Huge fallen limestone statue, ~10m (33ft) long | Symbol of the pharaoh's power and artistry |
Alabaster Sphinx | Beautiful sphinx carved from a single alabaster block | Showcases ancient Egyptian artistic skills |
Ptah Temple Remains | Scattered columns and foundations of the main temple | Once the spiritual heart of the city |
Mit Rahina Museum | Open-air display of artifacts and sculptures | Offers a unique, personal historical experience |
Proximity to Saqqara | Home to the Step Pyramid, just a short distance away | Allows for a comprehensive ancient Egypt day trip |
Is Memphis Egypt Worth Visiting? Here’s Why This Ancient City Still Matters Today
Memphis may not shine like Giza, but its calm ruins and deep history offer a rich, authentic experience. If you wonder where is Memphis in Egypt, it lies near Mit Rahina, just 20 km south of Cairo. Here’s why Memphis deserves your visit.
- Egypt’s First Capital: Founded by King Menes around 3100 BCE, Memphis united Upper and Lower Egypt, shaping the nation’s start.
- Giant Ramses II Statue: See the fallen colossus of Ramses II in the open-air museum at Mit Rahina. It’s over 30 feet long and a powerful symbol of ancient Egypt.
- Alabaster Sphinx: Nearby, admire a smooth, single-block alabaster sphinx, smaller but rich in history.
- Temple of Ptah Ruins: Walk among the scattered stones of Ptah’s temple, once a center of worship and crafts.
- Close to Saqqara: The Step Pyramid of Djoser is just minutes away, adding depth to your visit
- Quiet and Peaceful: Unlike busy tourist spots, Memphis offers a calm atmosphere, perfect for relaxed exploration.
- Easy Day Trip: Located close to Cairo, it’s a hassle-free trip for history lovers.
- Step Into History: Visiting Memphis connects you to Egypt’s origin story, where pharaohs first ruled.
- Open-Air Museum Experience: Explore artifacts and ruins under the
- Skip the Crowds: Enjoy a more personal visit, away from the selfie sticks and noise.
Memphis Compared to Other Sites
Feature | Memphis | Giza | Luxor |
Crowds | Quiet and peaceful | Very crowded | Busy with tour groups |
Main Attraction | The fallen Ramses II statue | Great Pyramid and Sphinx | Karnak and the Valley of Kings |
Best For | History lovers seeking calm | First-time visitors | Temple explorers |
Nearby Highlights | Saqqara Step Pyramid | Solar Boat Museum | Workers’ Village |
Memphis isn’t just ruins; it’s where Egypt’s story began. Where is Memphis in Egypt? Just south of Cairo, near Mit Rahina, it offers a unique, quiet glimpse into the ancient world. Pair it with Saqqara for a full day of history. Ready to walk where history whispers?
Book your Memphis tour with EgyptOnlineTour and experience history up close—or make it part of a full 10-day Nile cruise and pyramids trip for a deeper journey into Egypt’s past.
How to Get Around Memphis, Egypt: Simple Tips for Easy Travel Near Cairo’s Oldest Capital
Getting around Memphis is quick and simple once you know what to expect. If you’re asking where is Memphis in Egypt, it’s near Mit Rahina, just 20 km south of Cairo. Below are the best ways to move around and enjoy your visit — and don’t forget to check the Grand Egyptian Museum ticket price if you plan to visit nearby.
- Arrive by Car: Most travelers use a private car or taxi from Cairo—it takes less than one hour.
- Book a Local Guide: Many guides offer round-trip transport with stops at Saqqara and Dahshur.
- Walk the Site: Once there, the open-air museum is walkable. Wear good shoes for rough paths.
- Hire a Tuk-Tuk: In nearby villages, tuk-tuks are fast and cheap for short rides.
- Pair with Saqqara: Since it’s close, combine both in one day. Guides often include both stops.
- Skip Public Buses: No direct public transport goes to Mit Rahina. Taxis are faster and safer.
- Use GPS for Clarity: Search “Mit Rahina” or Memphis, Egypt to guide your driver easily.
- Pack Water and Snacks: Few shops are nearby, so come prepared, especially in summer.
- Early Visits Beat Heat: Arriving early helps you explore more before the midday sun hits hard.
Memphis is small, quiet, and best seen on foot—just get there, and let history lead you. We want to hear about you to book your Egypt Tour Packages
Option | Description | Travel Time (from Cairo) | Estimated Cost (from Cairo) |
On Foot | Within the open-air museum area | N/A | Free |
Taxi | The fastest way to reach Memphis from Cairo | ~28 minutes | $2-$3USD |
Metro (Line 1) | Cheapest way to reach Memphis from Cairo | ~53 minutes | $1-$3USD |
Private Driver | Ideal for combining Memphis with nearby sites like Saqqara and Giza | Flexible | Varies (often part of the tour package) |
Organized Tour | Convenient option for a comprehensive exploration of the necropolis | Flexible | Varies (tour package) |
Features & importance of Memphis Ancient Egypt
Memphis was Egypt’s first capital and a major center for politics, religion, and trade. Understanding its features helps grasp Egypt’s early civilization. Here’s a clear, simple guide to what made Memphis special and why it still matters today.
- Served as capital during Egypt’s Old Kingdom for over 800 years
- Located on the Nile’s west bank, helping trade flow north and south
- Home of Ptah’s temple, the god of creation and artisans
- Held massive statues, including the fallen Ramses II colossus
- Close to Saqqara, where Egypt’s first pyramid was built
- Linked religion, politics, and trade, making it a central force in Egyptian life
- Now a UNESCO site, its open-air ruins still attract those tracing history’s roots
Ancient City of Memphis Museum: A Window into Egypt’s Past
The Ancient City of Memphis Museum offers a unique chance to explore Egypt’s earliest capital. If you wonder where is Memphis in Egypt, this museum near Mit Rahina reveals its rich history through impressive artifacts and open-air displays. You can also see it as part of the 10 Days Round Trip Nile Cruise and Pyramids tour, which covers Egypt’s top historical sites in one unforgettable journey.
- Open-Air Museum: Walk among giant statues, temple ruins, and stone blocks under the clear desert sky.
- Ramses II Colossus: See the massive fallen statue of Ramses II, a highlight that captures ancient royal power.
- Alabaster Sphinx: Carved from one piece of stone, this lesser-known sphinx is older than Giza’s and easier to view up close.
- Temple of Ptah Ruins: Explore the remains of Ptah’s temple, once a vital religious center.
- Historical Artifacts: Discover statues, stelae, and inscriptions that tell stories of pharaohs and daily life.
- Peaceful Atmosphere: Unlike crowded sites, the museum offers a quiet, reflective experience.
- Nearby Sites: Combine your visit with Saqqara and Dahshur pyramids for a full day of history.
- Easy Access: Located about 20 km south of Cairo, it’s a short trip for travelers.
- Educational Displays: Informative signs help visitors understand the significance of each ruin and artifact.
- Cultural Legacy: The museum preserves Memphis’s role as a political, religious, and economic hub.
This museum isn’t just a stop—it’s a living chapter of Egypt’s story, preserved in stone and sunlight.
It’s a must-see for anyone curious about where Egyptian civilization first took shape. You can include it in this 8-day Pyramids & Nile by Air tour
for a complete and effortless experience.
Memphis Egypt as a World Heritage Site: Why It Earned Global Recognition and Still Deserves a Visit Today
- Located near Mit Rahina, if you're asking where is Memphis in Egypt, this historic site is part of a UNESCO World Heritage listing. Below are key facts that show why it earned this honor.
- The first capital of Egypt, founded around 3100 BCE by King Menes.
- For centuries, it shaped the country’s governance, faith, and trade.
- Home to Ptah’s temple, once a major spiritual center in ancient Egypt.
- Surrounded by Pyramid Fields: Nearby lie the famous pyramids of Saqqara, Dahshur, and Abu Sir.
- The site features Open-Air Ruins, grand statues, and temple remains that show royal power.
- Named a UNESCO site in 1979 due to its outstanding cultural value.
- Offers a rare insight into ancient urban planning and sacred spaces.
- Still studied by archaeologists, discovering temples, tombs, and texts.
- Preserves Egypt’s oldest royal necropolis and burial traditions.
- A visit here connects you to discover where ancient Egypt truly began.
Why Was Memphis, Egypt, Abandoned? Key Reasons Behind the Ancient City’s Decline
Where is Memphis in Egypt? Memphis once flourished as Egypt’s first capital. However, over the centuries, it lost power, people, and purpose. Here’s why this great city was slowly left behind:
- Political Shift: When Thebes rose, rulers moved their courts away, leaving Memphis less vital.
- Religious Change: Moreover, Ptah’s cult faded as new temples gained favor in Upper Egypt.
- Economic Move: Next, Alexandria’s port drew trade north, so Nile commerce bypassed Memphis.
- River Silt: Over time, the Nile’s course shifted, thus making Memphis’s docks unusable.
- Earthquakes: Furthermore, tremors damaged key temples, and repairs proved costly.
- Stone Reuse: Then, conquerors stripped stones for new buildings, reducing Memphis’s grandeur.
- Desert Encroachment: In addition, windblown sand buried streets, thus discouraging return.
- Population Drift: Consequently, locals followed work to Cairo, leaving ruins behind.
- Roman Decline: Finally, Roman rule saw fewer resources, so Memphis faded into memory.
The Summary
Where Is Memphis in Egypt? You’ve uncovered its hidden gems and silent ruins. Now, step off the beaten path. Explore fallen statues under open skies, wander temple blocks, and feel 5,000 years of history come alive. Plus, EgyptOnlineTour makes it simple and safe. So pack your curiosity, book a local guide, and walk the world’s first capital yourself. Your adventure into Egypt’s heart starts today—don’t just read history, live it.
Frequently Asked Questions
1 What’s left of Memphis now? ▶
2 How old is Memphis? ▶
3 Is Memphis near the pyramids? ▶
4 Can I visit Memphis easily? ▶
5 What’s the best time to go? ▶
6 Who built Memphis? ▶
7 Why visit Memphis over other sites? ▶
8 Where is Memphis in Egypt? ▶
9 What is the Ancient City of Memphis Museum? ▶
10 Why was Memphis abandoned? ▶
Popular Categories
Related properties
Cairo, Aswan, and Luxor
-
Precio
$ 2,850
-
Tipo
Package
Cairo, Aswan, and Luxor
-
Precio
$ 1,850
-
Tipo
Package











